Word is starting to get out: Software often unnecessarily wastes a huge amount of energy. Several open source projects are developing tools for studying and measuring exactly how much. This article tours some of the most promising tools.
Taking a Tour
The Green Software Foundation (GSF), which the Linux Foundation launched in 2022, has the stated mission to “Build a trusted ecosystem of people, standards, tooling, and best practices for creating and building green software.” For this purpose, the GSF, which includes companies such as Microsoft, Intel, and Accenture, is organized into working groups. There are already several repositories with software, tools, and documents available on https://github.com/Green‑Software‑Foundation.
For example, the Open Source Working Group (opensource-wg) maintains a repository called Awesome Green Software with links to a whole host of tools and research articles on energy conservation, as well as links to useful free software. On top of this, you will find an overview of climate organizations, as well as access to free articles, papers, and books.
The GSF also highlights software for the cloud and machine learning. For example, there is a link to the Green Cost Explorer, a JavaScript tool that docks onto Amazon’s AWS Cost Explorer, but it also takes into account the energy types of the AWS regions as well as the costs. It ultimately shows you how much renewable (Green) and fossil (Grey) energy your cloud application requires.
Kepler, the Kubernetes Efficient Power Level Exporter, relies on eBPF to extract power-related statistics from Kubernetes. The Experiment Impact Tracker and the CarbonTracker measure the expected energy overhead for machine and deep learning jobs. The GitHub repository also has operating system-specific tools. For example, the Linux entry takes you to PowerAPI and PowerTOP.
Green Patterns
Anyone who is looking to make their own IT landscape greener will find what they are looking for in the Green Software Patterns repository. The GSF Patterns project collects tips and best practices for different fields of IT (AI, cloud, web). The spectrum ranges from very generic tips (e.g., run cloud jobs geographically as close to the user as possible) to concrete recommendations for action (e.g., compress transferred data). The patterns reference the Software Carbon Intensity (SCI) specification software and use simple formulas to show how admins and developers computationally implement the recommendations.
The specification helps to attach an SCI score to an application based on its CO2 emissions. The lower the value, the less climate-damaging gas the software causes. The SCI score maps CO2 emissions C per unit R, where a unit can be an API call, an additional user, or an ML training run. So the rough formula is SCI=C/R, where C can be further subdivided into more specific sources, such as O (operational emissions) and M (embodied emissions). O is the energy required by the software itself, and M is the proportional energy required to produce and dispose of the underlying hardware.
The Carbon Aware SDK, on the other hand, is something that developers can integrate into their own applications to take advantage of fluctuating energy prices in an environmentally smart way. The Carbon Aware SDK, which you can use either at the command line or via web API, is often used with non-time-critical machine learning jobs. The SDK helps move workloads to other cloud regions where renewable energy is cheap at the moment. Alternatively, it helps to throttle back operations as a function of the type of energy. The people behind the project refer to CO2 reductions in the double-digit percentage range.
Green Coding
The tools of the GSF are available to everyone, but the foundation itself is based in the US and is primarily funded and maintained by US-based corporations. However, similar efforts are taking place in Europe. Green Coding Berlin, for example, is a German-based organization that believes digitalization will only have a positive impact on society if it is sustainable. Green Coding is looking to develop open-source measurement tools that determine the energy requirements of software and infrastructure. The aim is to create a community and an ecosystem centered around green software. To this end, Green Coding cooperates with the Sustainable Digital Infrastructure Alliance (SDIA), an alliance of several companies with a roadmap for a sustainable digital infrastructure.
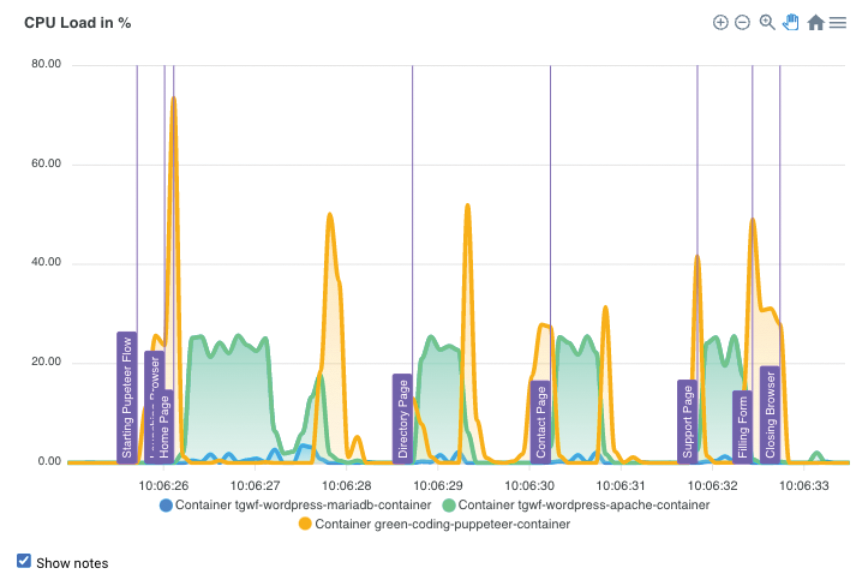
Green Coding offers the Green Metrics Tool, a container-based utility that is currently only intended for experimentation and testing. Green Metrics can help you measure the storage space per container, the CPU utilization as a percentage, or the system-wide power consumption. A Python API fields the metrics, and a JavaScript web front end visualizes the results (see figure).
KDE Eco
Green Coding collaborates with KDE Eco, a fledgling KDE initiative that aims to bring more sustainability to free and open software. The initial aim is to measure the energy requirements of free and open source software with a view to helping developers optimize software later on. The KDE Eco project offers two central repositories.
The FOSS Energy Efficiency Project (FEEP) is fundamentally based on the Blue Angel methodology. (Blue Angel is a German initiative that assigns a special label to designate environmentally friendly products.) The FEEP website describes a measurement setup that requires a reference computer, an energy meter, and software. This equipment helps to automate the execution of the software under test conditions and to record and process the measured data.
The BE4FOSS repository collects Blue Angel information and provides links to accompanying workshops and manuals. Anyone thinking of certifying their own software with the Blue Angel label can find help in the Blue Angel Application repository.
Conclusions
If you are seriously interested in software and energy saving, you will find many resources on the web; the examples presented in this article are a few of the projects working on the critical problem of energy efficiency. What is clear, however, is that many software efficiency projects are still in their infancy. As of now, the software community has no fixed standards for the measurement process or toolchains for integrating these capabilities into large infrastructures. Once these hurdles are removed, energy measurement tools could have a noticeable impact on software energy usage.
This article originally appeared in Cool Linux Hacks and is reprinted here with permission.
Want to read more? Check out the latest edition of Cool Linux Hacks.
See also:
- Creative Commons Surveys Open Climate Data Landscape
- How to Fight Climate Change with Open Source
- Open Source Projects to Help Measure and Manage Energy Use
- Visualizing the Open Source Sustainability Ecosystem
Contact FOSSlife to learn about partnership and sponsorship opportunities.








Comments